The complex interaction between hosts and pathogens influences the field of infectious diseases, guiding the processes of identification, penetration, and control within host cells. From the subtle invasion of bacteria and viruses to the significant changes in host cell activity and disease development, understanding these connections is crucial for uncovering disease mechanisms and creating effective treatment approaches. In this highly detailed educational blog, we explore the identification and penetration processes of various pathogens, their influence on host cell activity, the occurrence of virus-induced cell alteration, and the diseases induced by pathogens in both animal and plant hosts.
Recognition and Entry Processes of Pathogens:
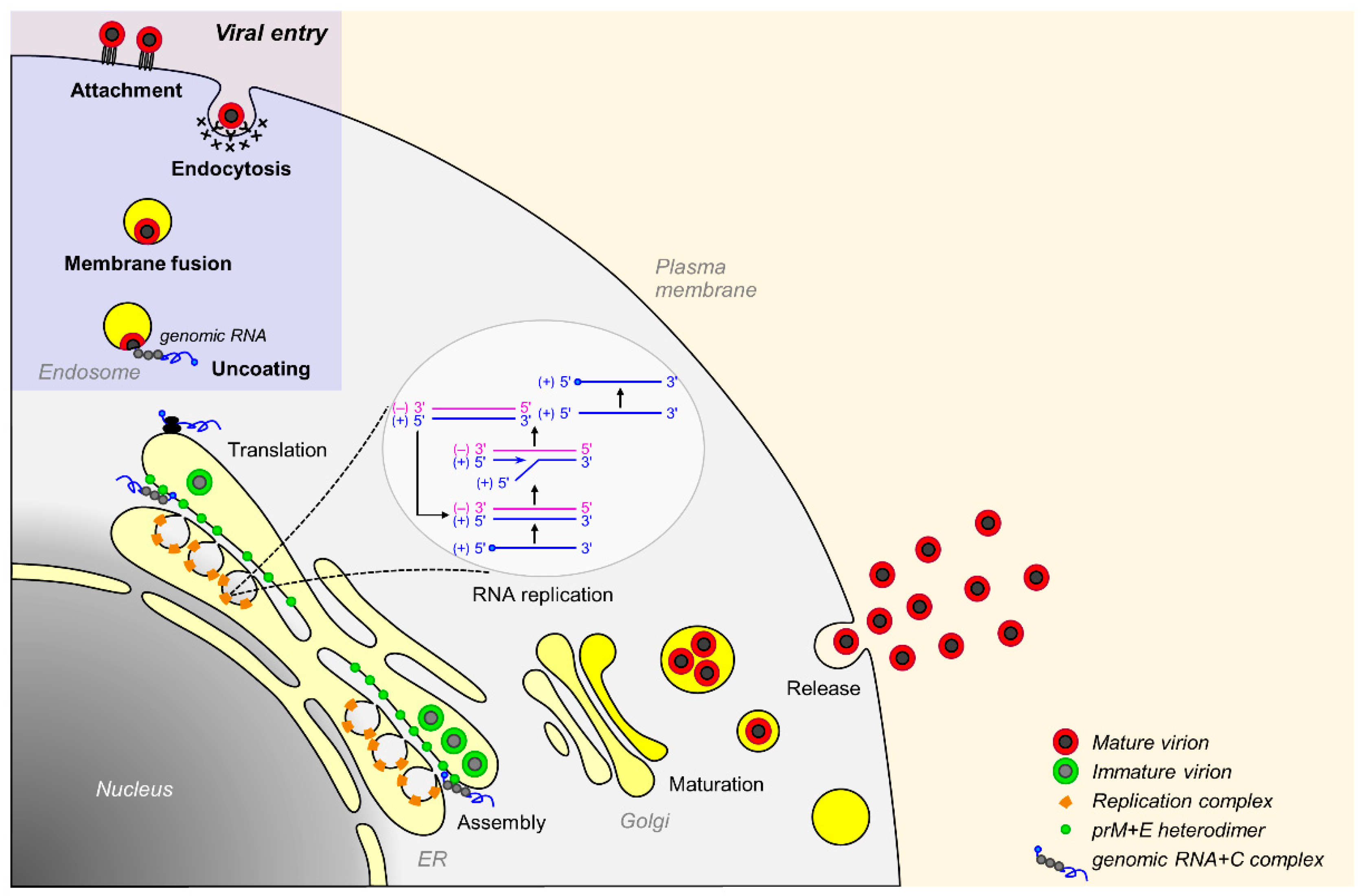
Viral Pathogens: Viruses use viral surface proteins to attach to particular host cell receptors, which helps the viruses enter the host cell through endocytosis or membrane fusion.
Alteration of Host Cell Behavior by Pathogens:
Intracellular Survival: Pathogens alter host cell signalling pathways, cytoskeletal dynamics, and vesicular trafficking to establish an intracellular environment suitable for their survival and replication.
Virus-Induced Cell Transformation:
Oncogenic Viruses: Some viruses can cause cancer by integrating their DNA into the host cell's genetic material, interfering with tumour suppressor mechanisms, and stimulating cell growth and survival.
Cellular Transformation: Cell transformation caused by viruses can result in the formation of cancers, including cervical cancer (which is triggered by human papillomavirus) and liver cancer (which is caused by hepatitis B and C viruses).
 |
Fig.- Hypothetical scheme of HCMV dispersal and its possible involvement in the development of breast cancer |
Attribution: Georges Herbein, Amit Kumar, CC BY 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
Pathogen-Induced Diseases in Animals and Plants:
Animal Diseases: Pathogens result in various illnesses in animals, such as bacterial infections, viral diseases, parasitic infestations, and fungal infections, which ultimately lead to sickness and death in affected hosts.
Plant Diseases: Plant diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and nematodes can have a severe impact on agricultural productivity and food security globally.
Cell-Cell Fusion in Normal and Abnormal Cells:
Normal Cell Fusion: Cell-cell fusion is a natural process that plays a role in fertilization, myogenesis, and placental development. This process is facilitated by fusogenic proteins and involves membrane fusion events.
Abnormal Cell Fusion: Pathogens like viruses and parasites have the ability to cause abnormal merging of cells, resulting in the formation of syncytium, which can lead to tissue damage and progression of disease.
Conclusion:
The interaction between hosts and parasites is intricate and ever-changing, influencing the development of infectious diseases and impacting cellular activity. From the initial recognition and entry of pathogens to the significant changes in host cell behavior and disease development, each aspect of these interactions provides understanding of the molecular mechanisms involved in infection and immunity. Understanding host-parasite interactions is crucial for the development of new treatments, vaccines, and methods for disease prevention and control, ultimately enhancing human and animal health and preserving global ecosystems. As we uncover the complexities of host-parasite interactions, we develop a greater understanding of the fragile balance between pathogens and their hosts in the constant struggle for survival and adaptation.
Tags
Animal Diseases
Bacteria
Biology
Cell Fusion
Education
Host Cell Alteration
Host-Parasite Interaction
NET Lifesciences
Pathogen-Induced Diseases
Plant Diseases
Science
Virus-Induced Transformation
Viruses